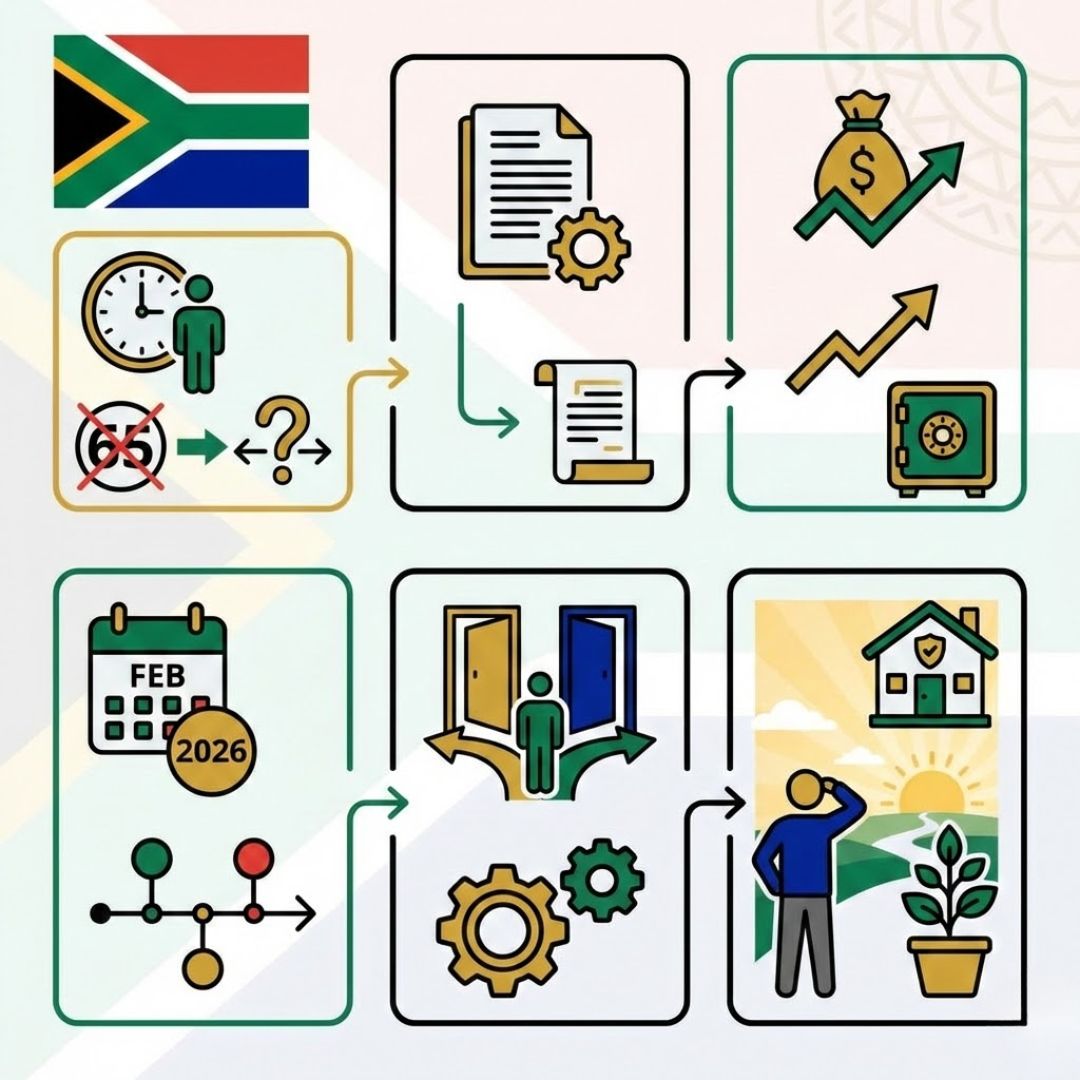
South Africa is preparing for a major shift in how retirement is defined, as new pension rules from February 2026 move the country away from the long-standing idea of retiring at 65. The change reflects economic pressure, longer life expectancy, and the growing need to keep experienced workers active for longer. For many South Africans, this update is more than a policy tweak—it affects career planning, income security, and long-term financial confidence. Understanding what is changing, why it matters, and how it could affect you is now essential.

South Africa retirement age changes explained
The decision to move beyond the traditional retirement benchmark marks a clear break from changing retirement norms that shaped South Africa for decades. Policymakers argue that the current system no longer matches economic realities, prompting a gradual pension age shift rather than an abrupt cutoff. With people living longer and remaining healthier, the focus is turning toward longer working lives supported by updated pension structures. Officials stress that this is part of a broader policy reform timeline, giving citizens time to adapt while ensuring the pension system remains viable for future generations.

New pension rules starting February 2026
The updated framework will officially begin with the February 2026 rollout, introducing changes that affect when and how individuals can access pension benefits. While not everyone will be impacted immediately, there will be clear eligibility adjustments based on age, employment status, and contribution history. Revised contribution thresholds are designed to balance fairness with long-term funding needs, while the overall aim remains an income security focus for older citizens. Authorities emphasize that these rules are intended to strengthen, not reduce, retirement protection.
How the retirement shift affects workers
For employees, the new retirement framework influences everyday worker planning decisions, from career length to savings strategies. Employers are also rethinking employer workforce strategies, particularly in sectors that rely on experienced staff. The government is encouraging phased retirement options, allowing people to scale back gradually instead of stopping work suddenly. These changes are already prompting more open financial readiness conversations, helping households prepare earlier and with greater clarity for life after full-time work.
Understanding the broader impact
At its core, this reform responds to a growing demographic pressure reality that affects public finances and social support systems. By aligning retirement rules with sustainability goals, South Africa aims to protect pensions for decades to come. The shift also reshapes the future retirement landscape, encouraging flexibility rather than fixed milestones. For individuals, staying informed enables informed personal choices that reduce uncertainty and support a smoother transition into later life.
| Category | Previous Rule | New Rule (2026) |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Retirement Age | 65 years | Gradually increasing |
| Policy Start Date | Existing system | February 2026 |
| Pension Access | Fixed age-based | Flexible criteria |
| Work Options | Full retirement | Phased retirement |
| System Goal | Status quo | Long-term sustainability |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is retirement at 65 completely abolished?
No, 65 is no longer the fixed standard, but retirement becomes more flexible.
2. When do the new pension rules start?
The updated rules officially take effect from February 2026.
3. Will everyone have to work longer?
Not necessarily, as eligibility depends on individual circumstances.
4. Does this reduce pension benefits?
No, the aim is to strengthen pension sustainability, not cut benefits.




