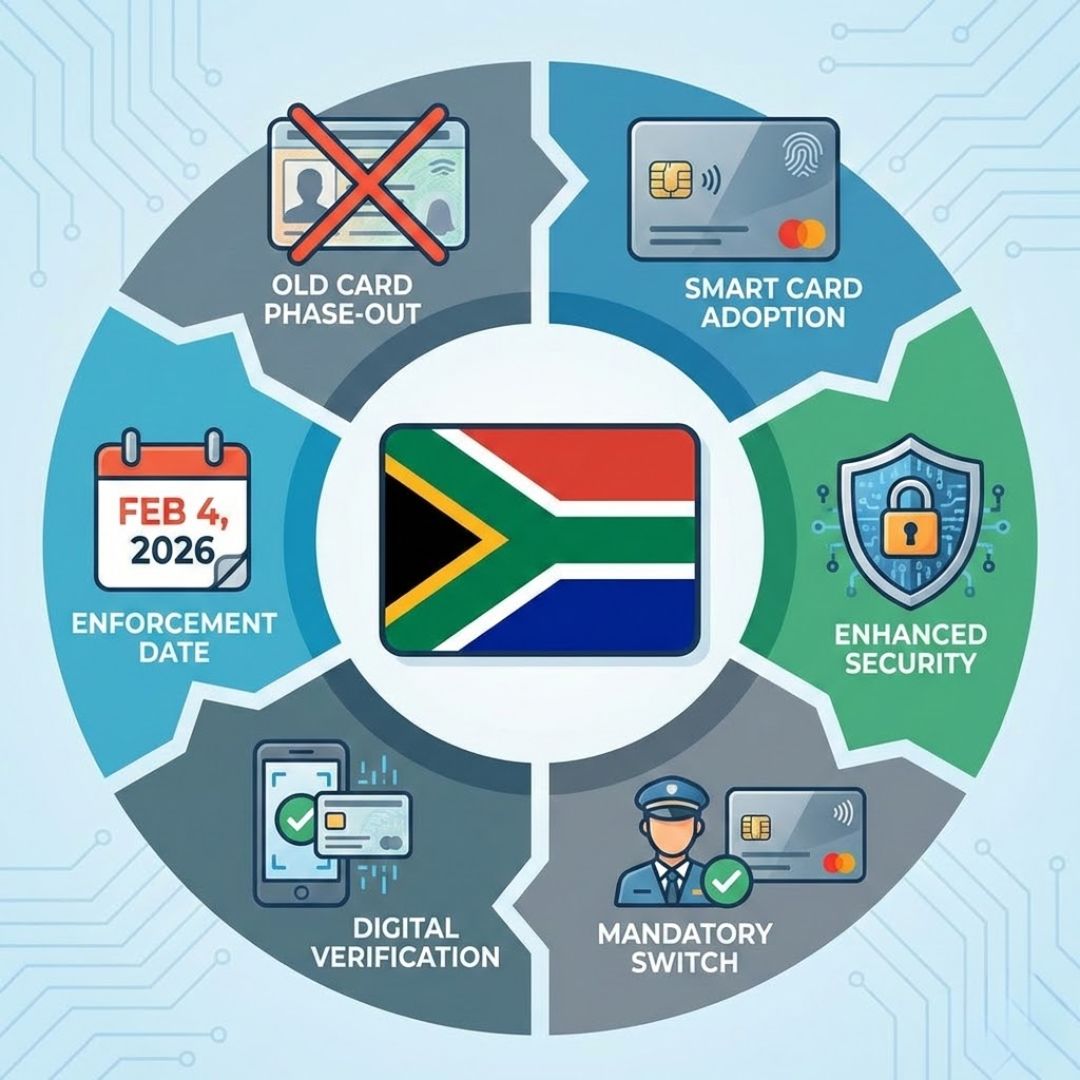
South Africa is getting ready for a big change in how drivers carry and use their licences as the country moves away from traditional driving licence cards. Starting from February 4 2026 motorists will switch to modern smart licences that offer better security & last longer. This change is part of a wider plan to update public services & stop fraud in the licensing system. The old cards will not vanish right away but drivers should learn how the new system works & what they need to do to follow the rules. The new smart licences use advanced technology to store driver information more safely than the current cards. These licences will be harder to copy or fake which should help reduce identity theft and licence fraud. The cards will also be more durable and resistant to wear and tear compared to the older versions that often fade or get damaged over time. Drivers will need to apply for the new smart licence when their current card expires or if they want to upgrade earlier. The application process will involve visiting a licencing centre where biometric data will be captured including fingerprints & a photograph.

South Africa’s Smart Driving Licence Rollout Explained
South Africa is preparing to introduce smart driving licences, a major upgrade for motorists nationwide. These new cards use advanced embedded technology to strengthen identity verification and significantly lower the risk of duplication. Authorities say the shift is designed to address long-standing challenges such as card damage and illegal reproductions. With features like enhanced security, digital identity checks, tamper-resistant construction, and a longer card lifespan, the smart licence is built for daily use. The rollout is set to begin in early 2026 and will follow a phased approach to prevent pressure on testing centres and administrative systems.

Why Traditional Licence Cards Are Being Replaced
Over time, conventional driving licence cards have shown clear weaknesses. Many motorists have experienced faded information, cracked plastic, or cards that are easily lost or misused. These issues make verification difficult and increase the risk of fraud. The new smart licence system aims to resolve these problems by offering stronger fraud prevention, secure handling of personal data, modern verification methods, and more durable materials. Officials also expect the change to improve interactions with traffic authorities and law enforcement. By adopting a standardised smart format, South Africa is aligning its licensing system with global best practices.
 Goodbye to Low Old Age Pension: Monthly Senior Payments Increase Up to R2,400 from 8 February 2026
Goodbye to Low Old Age Pension: Monthly Senior Payments Increase Up to R2,400 from 8 February 2026
What Motorists Need to Know About Smart Licences
For most drivers, moving to a smart licence should be a straightforward process, but some preparation will help. Applications will need to be submitted at approved centres, and motorists must ensure their personal details are accurate and current. The application process is expected to closely resemble existing renewal procedures, with the addition of enhanced security checks. Key advantages include faster identity verification, fewer card replacements, stronger legal standing, and potential future digital integration. Drivers are encouraged to follow official announcements to avoid missing important timelines.
Overall Impact and What to Expect Going Forward
The transition to smart driving licences marks a practical step forward for South Africa’s transport system. While any change can create uncertainty, the long-term benefits are clear. Motorists can expect simpler licence management, more reliable roadside checks, improved data accuracy, and greater trust in the system over time. As February 2026 approaches, staying informed will help drivers adjust smoothly. The gradual rollout is intended to reduce disruption while delivering a more secure and efficient licensing experience across the country.
| Feature | Old Licence Card | Smart Licence Card |
|---|---|---|
| Security Level | Basic protection | Advanced encryption |
| Durability | Easily damaged | High resistance |
| Fraud Risk | Higher risk | Significantly lower |
| Technology | None | Embedded smart chip |
| Replacement Frequency | Frequent | Less often |



